Key Takeaways
- The answer to how bad is porn for your brain lies in the fact that its endless novelty triggers unusually high dopamine spikes, which over time can reduce the brain’s sensitivity to everyday pleasures and rewards
- Frequent porn use can lead to desensitization, requiring more intense stimulation for the same response, and may affect motivation, focus, and emotional regulation
- The developing brain (under age 25) is especially vulnerable to habit formation from novelty-based content like porn, with increased risks for unrealistic expectations
- The brain is neuroplastic, meaning that it can rewire and recover when porn use is reduced or stopped, with improvements in dopamine sensitivity, focus, and emotional well-being over time
- Awareness, boundaries, and open conversations are more effective to stop porn and dopamine cycle than shame, especially for families navigating porn exposure with children and teens
Understanding what does porn do to the brain starts with understanding how the brain’s reward system works. Pornography triggers powerful neurochemical responses that can reshape how your brain processes pleasure, motivation, and everyday experiences. This guide explains the science behind how porn affects the brain, what happens with frequent use, and whether recovery is possible.
How the Brain’s Reward System Works
Before diving into how does porn affect the brain, let’s see the brain’s reward circuitry. It includes the dopamine spike, fueled by novelty, anticipation, and the fact that the brain is never fully used to it.
Dopamine is a key reason why people watch porn. It’s often called the “pleasure hormone,” but that’s misleading. Dopamine is actually the brain’s motivation and learning chemical. It signals “this is important — pay attention and remember this.” When you encounter something rewarding, your brain releases dopamine to reinforce the behavior and motivate you to seek it again.
Novelty is another thing what does porn do to the brain, as it responds strongly to new, unexpected, or surprising stimuli. They trigger larger dopamine releases than familiar ones. This makes evolutionary sense: discovering new resources increased survival chances.
Anticipation amplifies this effect and fuels why do people watch porn. When you expect something good but don’t know exactly when you’ll get it (like scrolling through content), dopamine spikes higher than if the reward were predictable. This creates a powerful loop: seek, find, spike, seek again.
Never enough is the critical part: the brain never fully adapts to novelty. While you might get bored with the same meal, introducing endless new options keeps dopamine firing. This is why buffet restaurants and endless-scroll platforms are so engaging — they exploit the brain’s sensitivity to variety.
How Porn Affects Dopamine and Reward Pathways
Study after study suggests porn is like a drug, dialing into your reward pathways and releasing chemicals like oxytocin and dopamine into your brain. Since neurochemical systems are mainly affected by porn-triggered dopamine and reward pathways, let’s explore what does porn do to your brain in this regard.
Research suggests pornography can trigger dopamine releases that rival or exceed those from natural rewards like food or social connection. Why? Because porn combines multiple dopamine triggers simultaneously: visual novelty with every click, sexual stimulation (one of the brain’s most powerful reward systems), anticipation during searching, and instant accessibility with no effort or social risk.
But is porn bad for your brain because of that? Well, unlike real-world sexual experiences requiring social skills and vulnerability, porn delivers intense stimulation immediately and endlessly. This creates an artificially amplified reward signal the brain wasn’t designed to process regularly.
This is why many people report spending far longer viewing porn than intended. The brain keeps seeking “just one more” in pursuit of that perfect dopamine hit, creating what researchers call a “seeking loop.”
With time, neural pathways associated with porn use strengthen. The question is watching porn normal is no longer there: the baseline for “exciting” shifts upward, making everyday pleasures less satisfying by comparison.
This brings us to desensitization, which explains is watching porn bad for you. When the brain is repeatedly flooded with artificially high dopamine levels, it compensates by reducing dopamine receptors (fewer receptors mean less sensitivity), lowering baseline dopamine production, and increasing the threshold for arousal.
That’s how regular porn watching builds dopamine and reward pathways that lead to desensitization. That’s why frequent porn users often experience effects of porn on the brain as needing “more extreme” content over time to feel the same arousal they once experienced with less intense material. It’s neurobiology, as the brain is adapting to its environment.
What Happens With Frequent Porn Use Over Time
Reduced sensitivity to pleasure, changes in motivation and focus, and habit formation are what happens with regular, long-term use and why is porn bad for your brain.
1. Reduced Sensitivity to Pleasure
One of the most frequently reported effects of porn on the brain is anhedonia — reduced ability to feel pleasure from everyday activities. When your brain becomes accustomed to intense dopamine spikes from porn, normal pleasures start feeling flat by comparison.
This dopamine tolerance is why understanding how to stop watching porn is so hard. It creates a negative feedback loop: as everyday pleasures feel less satisfying, the pull toward porn becomes stronger. Many people describe feeling like they’re “going through the motions” in daily life while porn becomes increasingly central to their sense of reward.
2. Changes in Motivation and Focus
Does watching porn affect your brain‘s ability to stay motivated? Research suggests yes, particularly with frequent use. When dopamine pathways become dysregulated from repeated high-intensity stimulation, tasks requiring sustained effort feel more difficult and less rewarding. The brain has been trained to prefer immediate, high-intensity rewards over delayed, effort-based ones.
The rapid-fire novelty of porn can condition the brain for constant stimulation. Focusing on single tasks for extended periods becomes harder. Some users report difficulty concentrating on books, conversations, or work without seeking distraction. Also, porn in relationships becomes a problem,
3. Habit Formation and Compulsive Patterns
The brain learns through repetition. Every time you follow the pattern — feel stressed, watch porn, feel relief — you’re strengthening a neural pathway. This is the cue, craving, reward loop that drives habit formation.
Over time, this loop becomes automatic. The cue immediately activates the craving, and before you’re consciously aware of deciding, you’re already reaching for your device. This is why is watching porn bad for some people — you’re working against ingrained neural patterns that make stopping harder than expected.
For some, porn use progresses beyond habit into compulsive territory, when understanding how to block porn becomes the only way out of a vicious cycle.
When Porn Addiction Becomes Destructive
Pornography addiction becomes destructive when it impairs psychological well-being, relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life, with recent research establishing strong associations between problematic pornography use (PPU) and mental health crises. Let’s see the exact destructive effects of pornography on the brain, including emotional regulation and well-being.
Porn, the Brain, and Emotional Regulation
One of the less-discussed arguments how bad is porn for your brain refer to emotional regulation — how we process and manage our emotions.
Many people initially turn to porn for stress relief, and it can work short-term. The problem emerges when porn becomes the primary stress management tool. Instead of developing a range of coping strategies, the brain learns a single shortcut: feel bad, watch porn, feel better (temporarily).
This creates stress dependency, where the brain struggles to regulate difficult emotions without porn. Minor frustrations that most people navigate with resilience become triggers for compulsive porn use because the brain hasn’t developed alternatives to porn-related coping pathways.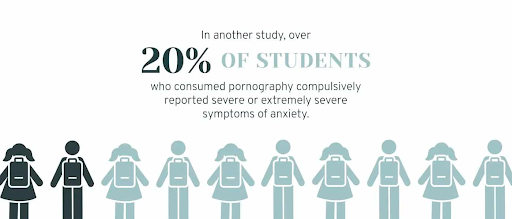
Porn and Mental Health: Depression, Anxiety, and Quality of Life
Beyond specific neurological effects of porn on brain function, there’s a broader question: is watching porn bad for you overall, considering mental health and well-being?
Research has found associations between frequent porn use and several concerns. Studies show correlations between heavy porn use and higher rates of depression and lower relationship and sexual satisfaction. When porn use becomes compulsive, it can displace activities that genuinely contribute to well-being — social connection, exercise, hobbies, sleep.
For many, the most damaging aspect isn’t the porn itself but the shame, guilt, and secrecy surrounding it. Living a double life and feeling unable to stop despite wanting to can be psychologically devastating.
How Porn Affects the Developing Brain (Kids & Teens)
Children and adolescents are highly vulnerable, so it’s important to understand how does porn affect the brain for them. Their dopamine system is highly active, which is why teenagers are naturally more risk-taking and sensation-seeking. This makes porn particularly powerful for young brains.
Being more impulsive, more reward-seeking, and less able to weigh long-term consequences, teens watching porn and children watching porn are especially responsive to porn-related novelty and reward. What might be moderately engaging for an adult brain can be overwhelmingly compelling for an adolescent one.
Beyond the neurochemical effects of pornography on the brain, porn exposure during developmental years can shape beliefs and expectations about sexuality, relationships, and bodies in ways that don’t match reality. Young people whose primary sexual education comes from pornography may develop distorted expectations about sexual performance, body image issues, a confused understanding of consent and boundaries, and difficulty with real relationships.
If you encounter this problem, your goal isn’t to shame young people or catastrophize porn exposure. Acknowledge that developing brains are more vulnerable and that early education, open conversations, and appropriate boundaries can make a significant difference.
Porn, Neuroplasticity, and Rewiring the Brain
Neuroplasticity is why we can learn new skills and adapt to changing environments. Every repeated behavior physically changes the brain by strengthening some neural connections and weakening others. Practice strengthens pathways, disuse weakens them, and the brain prioritizes efficiency
But how does porn affect the brain’s neuroplasticity? If you repeatedly watch porn while stressed, your brain wires “stress” and “porn” together. Eventually, stress itself becomes a trigger that automatically activates the craving for porn. These wired associations explain why breaking compulsive porn habits can feel so difficult — but why anyone can quit, too.
Can the Brain Recover After Reducing or Stopping Porn?
Here’s the hopeful part: neuroplasticity works in both directions. Just as the brain can wire itself toward porn dependency, it can also rewire itself away from it. When you stop or significantly reduce porn use, you stop what does porn do to the brain: old pathways weaken through disuse, new pathways strengthen as you practice alternatives, and dopamine sensitivity recovers.
When you stop flooding your brain with artificially high dopamine spikes, the reward system gradually recalibrates. Dopamine receptors that were downregulated during frequent porn use can increase in number and sensitivity. This process is sometimes called a “dopamine reset.” As receptor density increases, natural rewards start feeling satisfying again.
How long does it take to reverse the negative effects of porn on brain? Well, the timeline varies widely. Some people report noticeable improvements within weeks. For others, particularly those with years of heavy use, it may take months. But the consistent pattern is: with sustained abstinence or significant reduction, dopamine sensitivity improves.
As the brain recovers from constant novelty-seeking and instant gratification, many people report improvements in attention span, motivation for effort-based rewards, and mental clarity.
Why Awareness and Boundaries Matter (Especially for Families)
Understanding what does porn do to the brain isn’t about creating fear or shame — it’s about informed decision-making and protecting developing minds.
Research consistently shows that shame is counterproductive. It doesn’t prevent problematic behavior; it drives it underground. The most effective approach is open, shame-free awareness. Understanding how the brain responds to porn helps people make informed choices.
Particularly for Internet safety for kids and adolescents, this means creating environments where children can ask questions and talk about what they encounter online without fear of punishment. This doesn’t mean panic or over-restriction, but thoughtful, age-appropriate limits like filters and monitoring tools, device-free zones and times, and ongoing conversations. Kids who feel safe discussing porn exposure are more likely to come to parents early rather than develop hidden compulsive patterns.
Understanding how porn affects the brain is the first step. The next step is creating an environment that supports healthy brain development for your whole family.
The most effective approach for families should combine:
- Appropriate education: Age-appropriate conversations about brain science and healthy relationships
- Clear boundaries: Reasonable limits on access to harmful content
- Modeling: Adults being honest about their own digital habits
- Tools: Filters and accountability systems like Canopy porn blocker.
Canopy provides comprehensive content filtering, real-time monitoring, and accountability tools that work across devices and platforms — giving you peace of mind while respecting growing independence. Try it to protect your brain and mental well-being!
What Does Porn Do to the brain and other FAQs
What does porn do to the brain?
Among the negative effects of porn on the brain, it triggers high dopamine spikes by combining sexual stimulation with endless novelty. Over time, frequent porn use can lead to dopamine desensitization, where the brain reduces dopamine receptor density and requires more intense stimulation to feel the same arousal or satisfaction.
Also, what does porn do to the brain includes affecting motivation, focus, and emotional regulation, causing depression, and harming the ability to enjoy everyday pleasures. The brain’s reward system adapts to repeated high-intensity stimulation, sometimes creating compulsive patterns that are difficult to break.
How does porn affect the brain over time?
With frequent use over time, porn effects on brain include reduced sensitivity to pleasure (dopamine tolerance), decreased motivation for effort-based rewards, shortened attention span, and stronger habit formation around porn use. Some users report emotional numbing, difficulty connecting in real relationships, and needing increasingly extreme content to feel aroused, among how does porn affect the brain.
Thanks to the brain’s neuroplasticity, it adapts to whatever it repeatedly experiences — and if that’s high-intensity, novelty-based sexual content, neural pathways wire accordingly.
How does porn affect the brain with dopamine?
High dopamine spikes are why is porn bad for your brain. They combine multiple reward triggers: sexual stimulation, visual novelty, and the anticipation of finding “better” content. With repeated exposure, the brain compensates by reducing dopamine receptors (desensitization) and lowering baseline dopamine production.
This is a key aspect of porn and dopamine interaction that leads to porn brain damage in some cases.
Does porn rewire the brain?
Due to neuroplasticity, negative effects of pornography on the brain can be lasting and damaging. Repeated porn use strengthens neural pathways associated with porn-seeking behavior and can create strong automatic responses to triggers like stress or boredom. The porn brain damage means that it literally “wires together” the associations between certain cues and porn use.
The good news: this process works in reverse. When you stop or reduce porn use, those pathways weaken over time while new, healthier pathways strengthen.
Is porn addictive to the brain?
Regarding what does porn do to your brain, it’s clear that porn can create compulsive patterns that look very similar to behavioral dependence. They include loss of control, continued use despite negative consequences, tolerance (needing more intense content), and difficulty stopping.
Whether this qualifies as clinical addiction depends on definitions, but the lived experience for many people matches compulsive patterns. The brain’s reward system responds to porn and dopamine in ways that can create dependency, particularly when porn becomes the primary coping mechanism for stress or emotional discomfort.
Is porn bad for the developing brain?
The developing brain — particularly under age 25 — is especially vulnerable to porn effects on brain function because the prefrontal cortex (responsible for impulse control and long-term planning) hasn’t fully matured. Adolescent brains are more responsive to novelty and reward, making porn’s dopamine spikes particularly powerful. This is why is porn bad for your brain during these critical developmental years.
While not every young person who encounters porn will experience problems, the developing brain is neurologically more susceptible to compulsive patterns and lasting neural changes from high-intensity stimulation.